
How Do Electric Bikes Work?
Electric bikes—often called e-bikes—are revolutionizing the way we move, offering a greener, more efficient way to travel while still keeping you active. But how exactly do these high-tech two-wheelers work? If you've ever wondered how an e-bike gives you that extra push up a steep hill or lets you cruise effortlessly on your morning commute, you're not alone. In this guide, we’ll break down the core components of an electric bike, explain how they work together, and show you why e-bikes are fast becoming the go-to choice for riders of all ages and experience levels.
How do electric bikes work?

Electric bikes work by combining your pedaling effort with motorized assistance. When you start pedaling, a sensor (either cadence or torque) detects your motion or effort and activates the electric motor. The battery supplies power to the motor, which in turn helps drive the bike forward. A controller or display allows you to adjust how much assistance you receive. All these components—motor, battery, and sensor—work together to make riding smoother, especially on hills or longer commutes. You still need to pedal, but the bike makes it significantly easier and more efficient.
Core electric bike working principle

The core principle behind how electric bikes work is pedal-assist—a system where the motor only engages when you’re actively pedaling. Unlike a throttle-based electric scooter or moped, an e-bike doesn't move on its own. Instead, it amplifies your own effort, making cycling easier and more efficient without taking away the physical activity. This is what sets e-bikes apart as a hybrid between traditional biking and electric mobility.
When you start pedaling, sensors built into the bike detect your movement and send a signal to the motor to begin providing assistance. There are typically two types of sensors used in electric bikes:
-
Cadence sensors: These monitor whether the pedals are turning. As soon as you start pedaling, the sensor activates the motor to deliver a steady level of assistance. It's a more basic system and often found in entry-level or commuter e-bikes.
-
Torque sensors: These are more advanced and measure how hard you’re pressing on the pedals. The harder you pedal, the more assistance the motor provides, giving you a more natural and responsive riding experience. Torque sensors are commonly found in higher-end or performance-oriented models.
Once activated, the motor draws power from the battery and delivers it to the drivetrain, helping to rotate the wheels and propel you forward. The amount of assistance can usually be adjusted through a handlebar-mounted controller or display unit, allowing you to switch between different power modes depending on the terrain or your energy level.
Despite the electric help, you are always in control of the bike, and human effort remains an essential part of the ride. The electric motor simply makes cycling more manageable, allowing you to tackle hills, headwinds, and longer distances with greater ease. This pedal-assist system ensures that e-bikes still promote physical activity while reducing the strain that often comes with traditional cycling.
Key components of an electric bike

Electric bikes may look similar to traditional bicycles at first glance, but they’re powered by an intelligent system made up of several key components working seamlessly together. These components include the electric motor, battery, sensors, and a controller/display unit. Each plays a crucial role in delivering smooth, efficient pedal-assist performance.
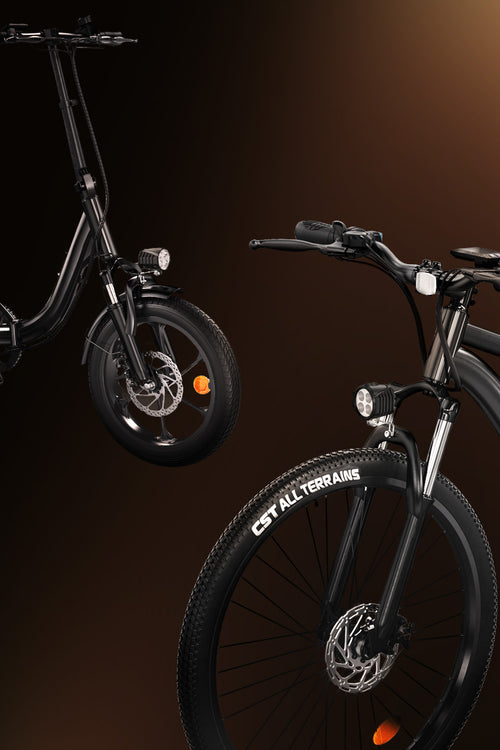
Electric bike motors

The electric motor is the core power source of an e-bike, responsible for delivering torque to assist your pedaling. Rather than taking over, the motor amplifies your effort—especially noticeable when tackling hills or riding into strong headwinds.
E-bike motors can be positioned in three main locations:
-
Front Hub Motor: Located in the front wheel hub, these provide a pulling sensation and are typically used in entry-level or folding bikes. They’re simple and easy to maintain.
-
Rear Hub Motor: Positioned in the rear wheel, these offer better traction and a more natural push-forward feeling. They’re common in commuter e-bikes.
-
Mid-Drive Motor: Located at the bike’s crankset (pedal area), these motors provide the most balanced weight distribution and the best performance on steep climbs or long-distance rides. They're popular in high-end models.
In the UK, electric bike motors are legally limited to 250 watts of continuous power when used on public roads. This ensures both safety and compliance with government regulations.
Electric bike batteries

The battery is the energy source for the motor. It stores electrical energy and feeds it to the motor when needed, powering the assist system. Batteries come in different capacities and types, which affects range, weight, and charging time.
-
Typical Charging Time: Between 2 to 8 hours, depending on the battery’s size and brand.
-
Placement: Most batteries are either integrated into the bike frame for a sleek look or mounted on the rear rack for easier removal.
-
Durability: A quality e-bike battery can last for up to 1,000 charge cycles, meaning you can ride thousands of miles before needing a replacement.
Battery efficiency and capacity are critical factors that determine how far and how long you can ride on a single charge.
Electric bike sensors
Sensors are the intelligent link between your pedaling and the motor. They determine how and when assistance is delivered by detecting your pedaling activity and effort.
There are two primary types of sensors used in electric bikes:
-
Cadence Sensor: Detects when you are pedaling. Once movement is detected, the motor engages at a consistent assistance level, regardless of how hard you're pedaling. It’s ideal for casual riders or flatter terrain.
-
Torque Sensor: Measures how much pressure you're applying to the pedals. The more effort you exert, the more power the motor provides. This results in a more responsive and intuitive riding experience and is ideal for hilly routes or technical terrain.
The type of sensor affects how natural and smooth the power delivery feels while riding.
Electric bike controllers/displays

The controller or display unit, usually mounted on the handlebars, acts as your command center. It lets you interact with the e-bike’s electrical system and monitor key performance data.
With the display unit, you can:
-
Turn the system on or off
-
Adjust the level of pedal assistance, usually through preset modes like Eco, Normal, or High
-
Monitor your speed, battery level, range, and sometimes even distance traveled
More advanced display units may include smartphone integration, navigation, and diagnostics. Regardless of complexity, the controller gives you full control over how much assistance the motor provides and allows you to tailor your ride to suit your needs.
Together, these components form the foundation of how an electric bike works. When properly integrated, they deliver a riding experience that’s smooth, powerful, and perfectly suited for a wide range of uses—from urban commuting to off-road adventures.
How do electric bike components work together
The magic of an electric bike lies in how its components seamlessly work together to deliver a smooth and efficient ride. When you begin pedaling, the sensors detect your motion or effort and send a signal to the motor. The battery then supplies the necessary electrical energy to the motor, which adds power to the bike’s drivetrain, helping to propel you forward with less physical strain.
This motor assistance kicks in instantly and adjusts based on the level of support you've selected through the handlebar-mounted display or controller. The display allows you to easily manage power levels, monitor battery status, and track your speed or range. The coordination between sensor feedback, motor power, and rider input ensures a responsive and natural-feeling ride—whether you're commuting, climbing hills, or just cruising on a weekend ride.
Performance factors
Several factors influence the overall performance of an electric bike, particularly its speed, range, and efficiency. In the UK, e-bikes are legally limited to a maximum speed of 15.5 mph when using pedal assist. Once this speed is reached, the motor automatically cuts out, and any additional speed must come purely from your own pedaling effort. This regulation helps maintain safety while still providing a helpful boost during your ride.
Beyond speed, the range and efficiency of an e-bike depend on a variety of elements. Your cadence, or how fast you pedal, plays a big role—maintaining a consistent cadence above 50 revolutions per minute tends to use energy more efficiently. Weight also matters; carrying extra cargo or riding with heavy gear puts more strain on the motor and drains the battery faster.
Frequent stopping and starting, such as in city traffic, consumes more energy compared to riding at a steady pace. Additionally, proper gear shifting helps the motor operate efficiently by reducing strain, especially on inclines. Lastly, tyre pressure affects rolling resistance; keeping your tyres properly inflated ensures a smoother, more energy-efficient ride. Paying attention to these performance factors can significantly extend your battery life and improve your overall riding experience.
Maintenance and lifespan
Electric bikes are designed to be durable and low-maintenance, especially when equipped with brushless motors, which are commonly used in modern e-bikes. Brushless motors have fewer moving parts that wear out, making them more reliable and efficient over time. While the motor itself typically requires very little upkeep, regular inspections are still recommended to keep the entire system in top condition.
Some e-bike brands recommend an initial check-up after around 4 weeks or 300 miles of use to ensure everything is functioning correctly, followed by regular maintenance at set intervals. Hub motors are particularly valued for their simplicity and reliability, often lasting up to 10,000 miles when properly maintained. As with any bicycle, keeping the drivetrain clean, tyres properly inflated, and storing the bike in a dry, sheltered location will help preserve performance and extend the overall lifespan of your e-bike.
Conclusion
So, how do electric bikes work? It all comes down to a smart system of motors, batteries, and sensors working in harmony to assist—not replace—your pedaling. Whether you're navigating city streets or taking on challenging trails, an e-bike makes the journey smoother, faster, and far more enjoyable. As the technology continues to evolve, e-bikes are becoming more powerful, efficient, and accessible than ever. Ready to ride the future? Now you know how it works.
FAQ
How do electric bike brakes work?
Electric bike brakes work just like those on a regular bicycle, using either disc or rim brakes to slow down the wheels. However, on many e-bikes, the braking system is connected to the motor through sensors. When you apply the brakes, these sensors instantly cut power to the motor, ensuring a smoother and safer stop. This feature helps prevent the motor from continuing to push the bike forward while you're trying to slow down. Despite the added weight of an e-bike, braking remains easy and reliable with proper maintenance.
How do electric bike gears work?
Electric bike gears work the same way as on a traditional bicycle. They allow you to adjust the resistance when pedaling, making it easier to climb hills or ride at higher speeds. You shift gears manually using a gear shifter on the handlebars. The difference with an e-bike is that the motor works alongside the gears, providing extra assistance based on the gear you’re in. For the most efficient ride, it's best to use lower gears when going uphill and higher gears on flat terrain, just like you would on a regular bike. Proper gear use also helps the motor run more efficiently and extends battery life.
How do electric bike controllers work?
Electric bike controllers are the brains of the e-bike’s electrical system. They manage the flow of power from the battery to the motor based on input from the rider and sensors. Typically located on the handlebars or built into the frame, the controller allows you to turn the motor system on or off, adjust the level of pedal assistance, and monitor key information like speed, battery level, and distance. When you change assist levels or start pedaling, the controller processes that information and tells the motor how much power to deliver, ensuring a smooth and responsive ride.
How do electric bike conversion kits work?
Electric bike conversion kits allow you to turn a regular bicycle into an e-bike by adding essential electric components. These kits typically include a motor (usually hub or mid-drive), a battery, a controller, and sometimes a display and pedal assist sensors. The motor is installed on either the front or rear wheel—or at the crank in mid-drive systems—while the battery is mounted on the frame or rack. When installed, the system works just like a factory-built e-bike: the motor provides assistance when you pedal, controlled by the sensors and display unit. Conversion kits are a cost-effective way to enjoy the benefits of electric cycling without buying a brand-new e-bike.
Do you still have to pedal an electric bike?
Yes, you still have to pedal an electric bike. E-bikes use a system called pedal assist, which means the motor only provides power when you’re actively pedaling. The motor is designed to assist, not replace, your effort—making riding easier, especially on hills or longer journeys. In the UK and many other countries, the law requires that e-bikes must be pedal-powered to be road legal. So while you’ll get a helpful boost, you’re still getting exercise and staying in control of the bike.
Do electric bikes charge when you pedal?
Most electric bikes do not charge when you pedal. While the idea of regenerative charging exists, it's typically found only in a few high-end models and is usually not very effective. Regenerative systems can recover a small amount of energy—mainly during braking or downhill rides—but it's not enough to significantly recharge the battery. For most e-bikes, the battery needs to be charged by plugging it into a wall outlet, just like a phone or laptop.
How long do electric bike batteries last?
Electric bike batteries typically last 2 to 5 years or about 500 to 1,000 charge cycles, depending on the battery type, usage, and how well it's maintained. Factors like frequent deep discharges, extreme temperatures, and overcharging can reduce battery life. To make your battery last longer, it’s best to charge it regularly (but not excessively), store it in a cool, dry place, and avoid letting it completely run out of power too often. With proper care, your e-bike battery can deliver reliable performance for many miles and years.
Can electric bikes self charge?
Generally, electric bikes cannot self-charge while riding. Although some advanced models feature regenerative braking systems that can recover a small amount of energy when slowing down or going downhill, this only adds a minimal amount of power back to the battery. The energy recovered is usually not enough to make a significant difference in your overall range. For most e-bikes, the main and most effective way to charge the battery is by plugging it into a wall outlet.
iScooter E Scooter Collections:
Electric Scooter | Kids Electric Scooter | Electric Scooter for Adults | Electric Scooter with Seat | Off-Road Electric Scooter | Foldable Electric Scooter | Girls Electric Scooter | 1000W Electric Scooter | 2000W Electric Scooter | Boys Electric Scooter | Dual Motor Electric Scooter | Big Electric Scooter | Electric Scooter with Suspension | Lightweight Electric Scooter | Commuter E-Scooters | 3 Wheel Electric Scooter
Show more ▼iScooter E Bike Collections:
Foldable Electric Bike | Affordable Cheap Electric Bike | Electric Bike for Adults | Electric Motor Bikes | Trek Electric Bike | Fastest Electric Bike | Electric Road Bike | Full Suspension Electric Mountain Bike | Giant Electric Bike | Womens Ladies Electric Bike | Mens Electric Bike | Electric Bike with Throttle | Electric Gravel Bike | Electric Mountain Bike UK | Fat Tyre Electric Bike | Electric Hybrid Bike | Electric Motorised Bike | Electric Push Bike | 1000W Electric Bike | Cool Electric Bikes | Electric Off Road Bike | Pedal Assist Electric Bike | Good Electric Bikes | Small Electric Bike | Trek Electric Mountain Bike | 2000W Electric Bike | Full Suspension Electric Bike | Mini Electric Bike | Road Legal Electric Bike | Step Through Electric Bike
Show more ▼👍 Buying Guide | 🚴♂️ Riding Guide
📋 Feature Guide | ❓ Common problem
Product category
Electric Scooter
Cheap Electric Scooters for Adults | Fastest Electric Scooter | Kids Electric Scooter | Mini Electric Scooter































































Article tags :
Leave us a message